Crack a Hash with John the Ripper
What is John the Ripper?
John the Ripper is a popular open-source password cracking tool used by security professionals, researchers, and ethical hackers to test the security of password hashes.
It is designed to help identify weak passwords, evaluate the strength of hash functions, and conduct security assessments.
John the Ripper supports different hash types including MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-512, and many others. This makes it versatile for various cracking scenarios.
The tool employs different types of cracking techniques, including dictionary-based attacks, brute-force attacks, and hybrid approaches. John the Ripper allows you to also use custom wordlists, applying different rules to transform words, and utilize incremental mode for brute-force attacks.
What is Hashing?
Hashing is a cryptographic technique that is used to transform data into a fixed-size output, typically for data integrity verification, password storage, and indexing. It is designed to be a one-way irreversible string that is computed based on a set algorithm.
A hash function takes an input or message and produces a fixed size hash value or digest. Regardless of the input size, the hash output is always the same length. Given the hash output, it’s computationally difficult to determine the original input.
Hashes should be efficient and quick to compute. They should also be collision-resistant, and rare for two different inputs to produce the same hash output.
Quick Demo on a Common Password
I created three different hashes of commonly used passwords using a tool I created in python to practice my python skills.
SOURCE CODE: https://github.com/jhyungleeCS/password-generator/blob/main/createpass.py
The program does a simple hash based on a password you provide and hashes it with a popular strong hashing algorithm, SHA-256.
Once hashed into a fixed string, the program then stores the hash into a txt file which is stored into the same directory that we are running the script on.
Three common passwords I've used for this example include:
- 123456
- password
- admin123
I went over to my kali box and downloaded the myeasypasswords.txt file. Net I ran the tool John the Ripper.
Root privileges are required for this tool. I ran the following command:
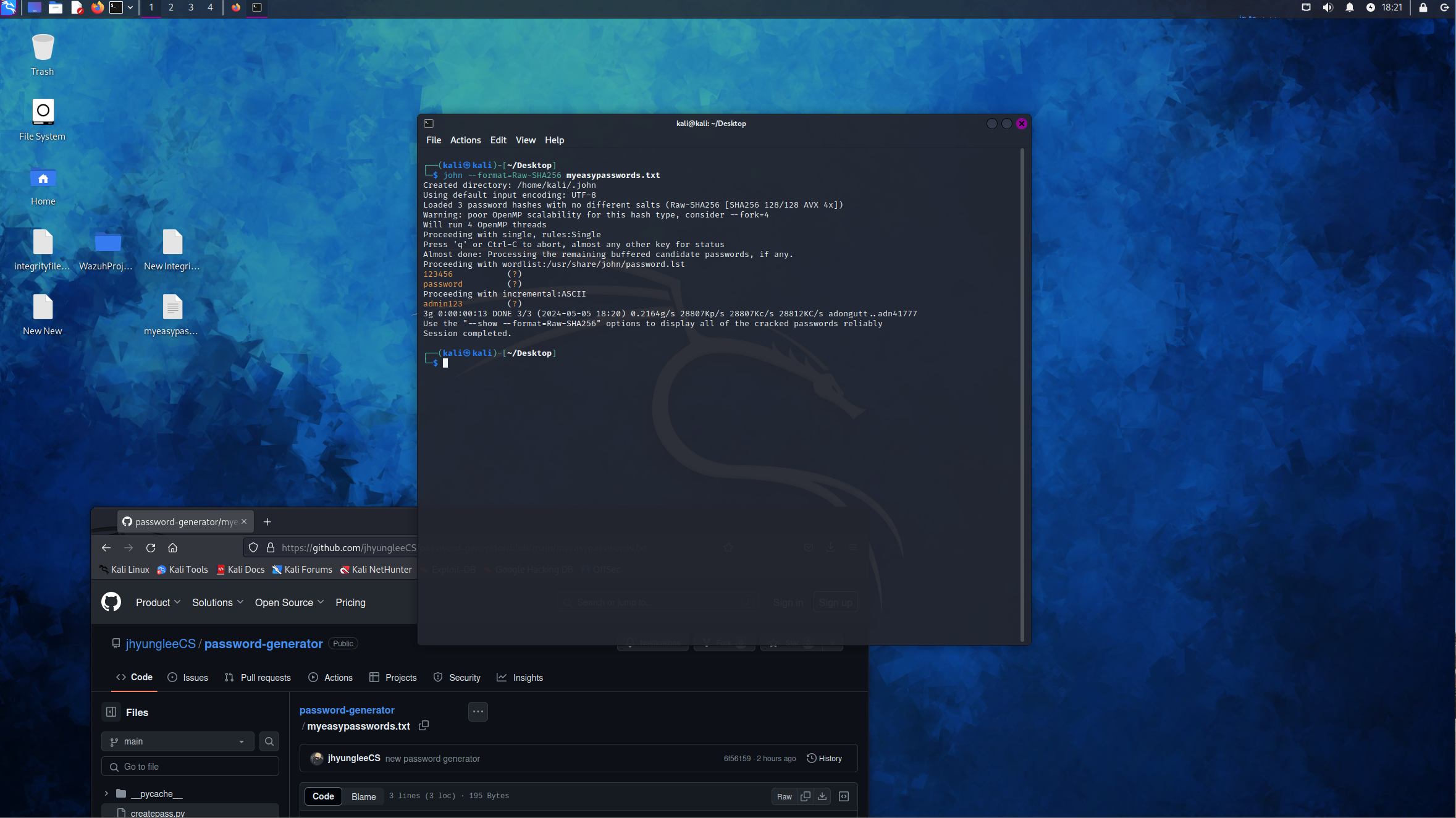
Within a a couple milliseconds, the program finishes easily cracking the passwords that I created.
The tool used a preconfigured list of common passwords, often referred to as a wordlist or dictionary. John the Ripper has a basic wordlist which contains a selection of commonly used passwords and password patterns.
However, users can also create or import custom wordlists. Custom wordlists can be larger and contain more diverse entries, such as commonly used passwords, dictionary words, common variations, or even words used for specific spear attacks.
There are cool tools out there including a python program called cupp.py that can be used to insert information about a victim and make a dictionary, custom wordlist to use for John.